Based on an industry report by market research firm Research Dive, analysts claim that the global agriculture robot market is reportedly expected to balloon by 400% in 2026. Originally valued at 4,082.8 million USD in 2018, early forecasts suggest that total industry value will eventually reach 16,640.4 million by 2026, while also recording a promising Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 19.2%.
By 2026, the same report has also suggested that the Asia-Pacific’s agricultural robot market will have the highest CAGR in the world, which is currently estimated at 19.7% with revenue of 3,798.3 million USD. Given this promising data, countries in the APAC region are taking note, and initiatives that aim to explore potential applications of robots in agriculture are underway.
Activity Sprouting in Singapore and China
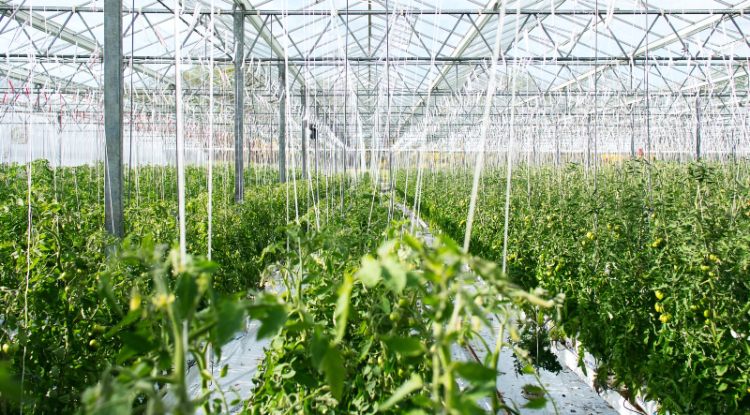
Despite being founded in a region not known for its agricultural activity, Singaporean agriculture developer Singrow has focused heavily on applying robotics and other related technology to address issues such as food security and agricultural sustainability. As reported by Techwire Asia, the company has already developed several technological models that integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI), some of which include the following:
- Automated Pollination: After a flower is automatically identified by a camera, agricultural robots will trigger a fan that toggles increased wind flow to encourage pollination effectivity.
- Infrared Scanners: These scanners identify strawberries which are then cross-checked with an existing Singrow database. Afterward, the agricultural robots can differentiate which strawberries are ready for harvesting and automatically pick them.
Similar to private companies like Singrow, governments are also at the forefront of including robotics in the agricultural industry as evidenced by the Singaporean government’s project: Agri-Food Cluster Transformation Fund (ACT). This initiative outright pledges an investment of 60 million SGD to exploring ways in which the domestic agri-food sector can increase overall productivity; a matter in which robotics is of the utmost relevance.
Like Singapore, the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) has also announced its commitment to exploring the deployment of technological solutions in China’s agricultural industry. Among its intention to improve seed varieties, grain yield, and overall agricultural sustainability, the CAAS will also work on the automation of processes through robotics. By doing so, the government-affiliated organization hopes to innovate traditional farming operations to reduce costs and increase supply chain efficiency.
For further insight on the potential application of robotics in other industries within Asia, subscribe to our newsletter here.




