Mobility as a Service (MaaS) integrates various transport and transport-related services into a single, comprehensive, and on-demand mobility service. Over the years, both public and private sectors have adopted MaaS services to solve the challenges of rapid urbanization, such as traffic congestion, transportation efficiency, high costs, and sustainability.
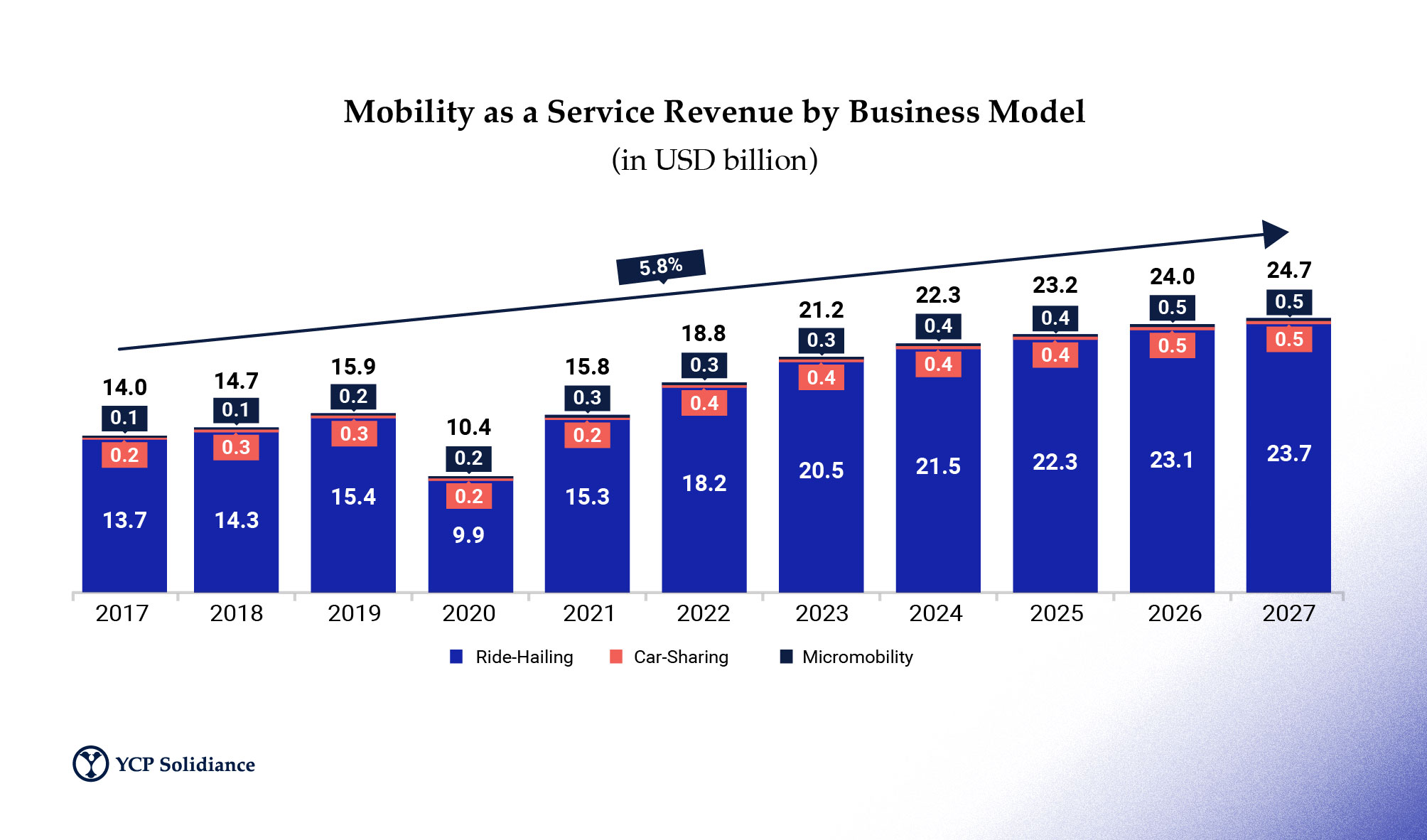
The mobility as a service market is broken down into three segments: car-sharing, ride-hailing, and micromobility. Car-sharing consists of car rental, sharing, and subscription services. On the other hand, ride-hailing allows users to book rides and pay via an app with a transportation network company (TNC), where the market comprises vehicle types, such as motorcycles and cars. Lastly, micromobility refers to the shared services of light vehicles such as motorbikes, scooters, and bikes.
Before the pandemic, MaaS development in Southeast Asia (SEA) was on an upward trend. However, the COVID-19 pandemic heavily impacted the industry. With restrictions lifted, industry growth has resumed, and the market is expected to expand exponentially over the next half-decade.
Experts predict several key drivers to propel the Mobility as a Service market forward. Across the region, governments have implemented tax incentives to encourage the development of MaaS services in building smart cities. Most tax incentives are geared towards the use of electric vehicles. Apart from this, the growing number of smartphone and internet users in SEA has paved the way for the development of MaaS. Accompanying this growth is the surge in e-commerce businesses and the expanding use of e-wallets for transactional purposes driving the industry forward. Developing highly secure and safe payment gateways is also expected to contribute to the growth of mobility as a service market during the forecast period.
While the MaaS market is undoubtedly full of potential, there are still barriers for MaaS development in Southeast Asia that can hinder overall growth for the market. The limited public transportation infrastructure is a common problem among many cities across the region. Inadequate transportation infrastructure makes it challenging to provide reliable MaaS services, making it difficult to attract new users. Another challenge is the need for a comprehensive legal framework. Governments have yet to provide clear guidelines on licensing, safety, and insurance requirements, hindering the scalability of services and integration.
Furthermore, operators must be equipped with the necessary technology to deploy a real-time information system to support commuters on their journey. The challenge comes in formatting the data and transmitting the information in an orderly manner, which are crucial in building user trust in the MaaS system.
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the MaaS market in SEA by diving deep into existing business models, drivers and barriers for growth, current market players, and key outlooks and trends. Download our free report today for further insights into how your company can enter and thrive in SEA’s growing MaaS market.
Author
Mehdi Jaouadi
Mehdi is a Partner based in Thailand, with over 14 years of experience in strategy formulation, business development, and large-scale expansion growth within Automotive, FMCG, Healthcare, and other sectors.
Recent White Paper
See All





