The China tire market is developing rapidly because of an effective industry overhaul primarily spearheaded by the government. In addition, the recovery of the global economy has allowed for the substantial success of domestic tire brands, which allows Chinese companies to become more competitive against global manufacturers.
To sustain this success in the long-term, interested stakeholders should become familiar with the Chinese tire market and its nuances, specifically, the factors leading to its initial growth and the current tire market structure. Read this excerpt from our latest white paper, Developing Long-Term Domestic Success: Insights on China’s Tire Market, which you can read in full here.
The Chinese tire industry, which has grown exponentially for more than a decade, has been facing a slowdown for the past three years. Tariff barriers imposed by the United States and European countries, as well as a huge overcapacity in domestic manufacturing, have led to regulations on the industrial structure and market environment. Although the overall domestic market size is expected to further grow at a slow pace, whether it can develop domestic brands that could compete with foreign tire brands that dominate the market for decades will be the key to the long-term success of the Chinese tire industry.
The Growth of the Chinese Tire Market
Since 2006, China has been recognized as the world’s number one tire producer, surpassing numbers from the United States. The rapid growth of new car sales has also led to China being named the world’s largest tire market in 2010, with numbers reaching an all-time high in 2016.
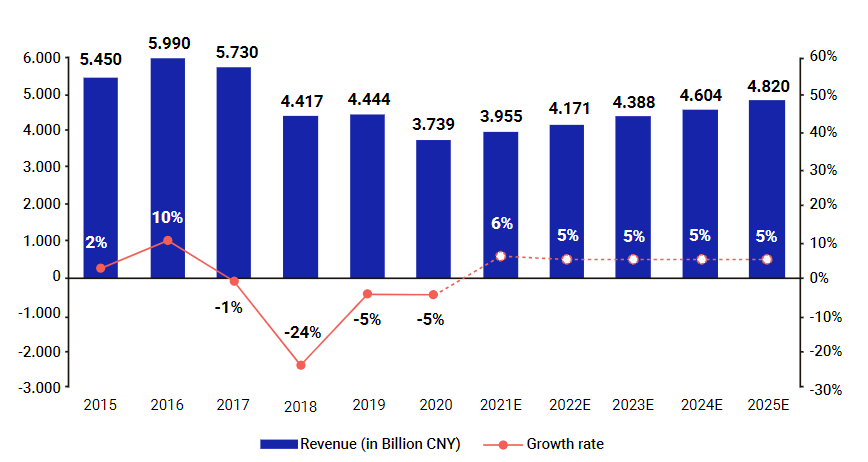
However, in 2017 China’s tire market began to drop aggressively due to the West’s anti-dumping tariff policies and the escalating China-U.S. trade war, which caused the size of the market to shrink by 38%.
To counter industry decline, the Chinese government issued “Tire Industry Entry Standards” in 2017, which raised the entry barrier for manufacturers. The government further reorganized the industry by bankrupting low-capacity and low-profit manufacturers to improve the capacity utilization rate and eliminate excessive price competition. At the same time local governments, such as the leaders of Shandong province, started funding leading local brands to improve competitiveness on the global market. By the end of 2021, the number of Chinese tire brands decreased by 50% to just 207.
Due to the effective industry restructuring and the steady recovery of the global economy in 2021, the China tire market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5% through 2025, reaching 482 billion CNY in total market size.
Current Structure of the China Tire Market
The Chinese tire industry caters primarily to the passenger vehicle market, which is three times larger than the market for commercial vehicles. This ratio is projected to remain largely unchanged.
The passenger car tire market is categorized into three segments: the Original Equipment (OE) market, Repair (REP) market, and Export market. Due to the development of the domestic car market and the global tire trade policy, the REP market is expected to expand to 40% of the total market size by 2025, reaching 193 billion CNY in value. In 2021, the United States, China’s largest tire importer, announced that the 88% tariff policy on Chinese tires would be extended to 2026[1], forcing local manufacturers to focus on developing the domestic market.
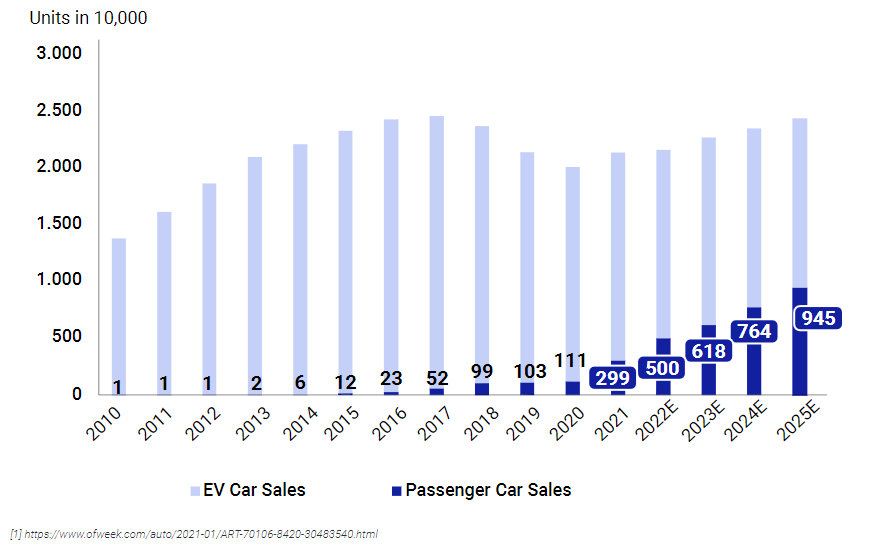
After rapid growth from 2010 to 2017, new car sales stagnated in China—however, the rapid growth and development of the electric vehicle industry has brought on a mild expansion of the domestic new car market. As new energy passenger vehicle sales achieved a breakthrough high in 2021, the overall new car market and the OE tire market is expected to grow at a 3~4% CAGR through 2025.
On the other hand, the number of registered cars is still increasing rapidly and expected to approach 400 million units in 2025. This is expected to drive up the needs of the domestic REP market to 4.5 billion units in the same year with growth at a CAGR of 12%. It is foreseen that the REP market will become the largest sub-market, accounting for 40% of the total market value, by 2025.
In addition, the use life of passenger cars changed in 2021 from a fixed 15-year period to a 600,000 km mileage limit, with tire testing becoming a mandatory part of car inspection programs. Both policies are expected to drive the REP market to higher growth in the long term.
To get further insight into other automotive trends current emerging in Asia, subscribe to our newsletter here and check out these reports:







