Last November 28, 2022, Santander UK held the “Building resilient supply chains between the UK and Asia – automotive/advanced engineering” webinar, the third session of their ongoing series on supply chains in Asia. The seminar featured a panel of supply chain and automotive experts from all over Asia, who shared their expert insight on the latest automotive industry trends.
Considering that the post-pandemic setting has further reinforced the need to build resilient global supply chains, several industries across Asia are adjusting to this trend. In Thailand specifically, the automotive sector has shown immense potential wherein electric vehicle development is quickly becoming a major focal point for industry players.
Acting as the representative for the ASEAN region, YCP Solidiance Director Nuttapan Meethong shared his insight on Thailand’s automotive market, its outlook, and the relevant industry trends that parties should look out for in 2023 and beyond.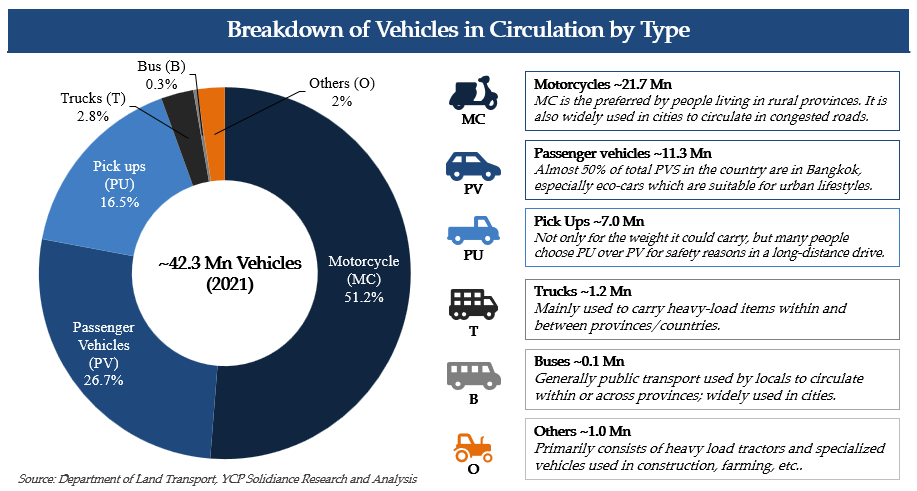
Overview of Thailand’s Automotive Industry
Currently, Thailand is the second-largest economy in Southeast Asia and its GDP is expected to grow even further at a 5.4% CAGR from 2021 to 2025, eventually reaching a value of 632 billion USD within the same period. These statistics suggest that Thailand and its professional industries, like automotive, are well-positioned for success in Asia and across the globe.
When analyzing the composition of the Thai automotive market, there are approximately 1800 companies in the automotive sector, this includes 30 to 40 major companies, around 700 Tier 1 automotive part producers, and over 1000 Tier 2 and 3 producers. The presence of these stakeholders not only signifies that the current automotive supply chain is vast but more importantly, that it is primed for further industry growth due to its dynamic market structure.
In terms of total vehicles in circulation, there are approximately 42 million vehicles in Thailand as of 2021. Due to factors like practicality and affordability, more than 50% (~21 million) of the market consists of motorcycles. Following closely behind are passenger vehicles and pickups at ~11.3 million and ~7 million, respectively. Recent statistics reveal that Thailand is averaging 2.5 to 3 million newly registered vehicles annually, which totals 5-6 % of the total vehicles in circulation; this presents a unique growth opportunity for aftermarket players in the country.
For Thailand’s aftermarket market structure, automotive parts are generally distributed from the manufacturers through importers, master distributors, and wholesalers, or are made available directly to consumers via retailers. Several retail channels are utilized to facilitate these sales, like automotive part shops, chain workshops, independent workshops, original equipment suppliers (OES) shops, etc. The independent workshops and OES are the most prominent of these players as they have the most volume flow at 49% and 30%, respectively. 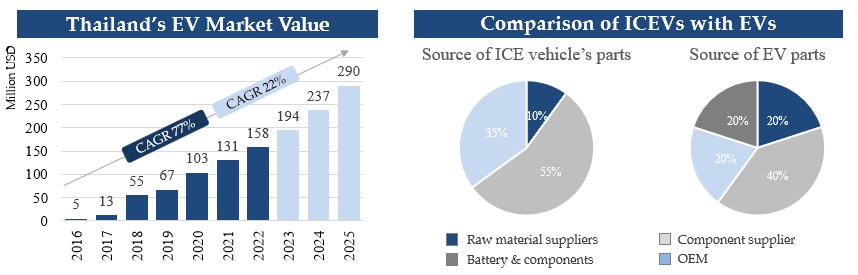
Implications of the Electric Vehicle Trend
The number of electric vehicles (EVs) across the world is increasing rapidly, thus signifying that automotive players are heavily invested in the electrification of the industry.
The EV trend is expected to drastically impact the automotive supply chain in Thailand as the production of EVs will require automotive components that are different from those that are currently utilized in the ICEV production process. For instance, components like exhaust systems and gearboxes will no longer be needed, while demand for electric parts will only continue to increase.
While this is a positive development as some parts and equipment manufacturers will still be compatible with the EV production process, others who are not may need to redevelop their operations or expand into other markets. Moving forward, part manufacturers should adjust their strategies to accommodate the needs of EV assemblers. This is expected to have a significant impact on the following industries: (1) electric components, (2) batteries, (3) wire and cable, and (4) tires.
Bolstering Growth of Electric Vehicles
Given that Thailand’s EV market is expected to register a 22% CAGR from 2022 to 2025, the domestic industry will likely focus on aspects like manufacturing and production to sustain the industry’s accelerated development. The market will be dynamic as both international and Asian brands will look to increase their market share, while also expanding through EV-related initiatives such as EV plants and battery manufacturing.
To ensure that the EV industry secures long-term success, the continued development of infrastructure will be an important area. Aside from scaling the production of EV components like batteries and the vehicles themselves, Thailand will also look to increase the number of ports and charging stations. As of early 2022, there are approximately 1,000 EV charging stations, with approximately 50% located in the Bangkok area. By 2030, Thailand aims to have 12,000 charging points available across its regions.
The role of the public sector will also be essential in supporting the success of EVs in Thailand as the Thai government has already launched several initiatives centered on EV adoption and manufacturing. Under the 30:30 electrification policy, Thailand aims to have zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs) to comprise at least 30% of all new vehicles produced by 2030. Other EV-related initiatives include purchasing subsidies, tax reductions, incentives, and exemptions. The schemes enacted by the government will support both the supply and demand of EV products.
In the coming years, all indicators suggest that EVs will continue to trend and fundamentally transform the landscape of Thailand’s automotive industry. This trend will manifest not only in consumer purchases but perhaps, more importantly, will inform the strategies of automotive players in terms of manufacturing, production, and the overall supply chain.
To get further insight into other automotive industry trends that will become relevant within Asia this 2023, subscribe to our newsletter here and check out these reports:






